DDM Company provides surveying services and carbon sequestration data compilation in forestry and agriculture sectors using Remote Sensing technology. This includes surveying through high-resolution satellite imagery, aerial photography mapping from drones, and also offers tree sample data collection using certified techniques (Verra, T-ver) for carbon credit registration for interested parties. With over 10 years of experience in environmental data management using Remote Sensing technology.
DDM ensures its clients that the survey data can be registered for carbon credit, either domestically (T-ver) or internationally (Verra).
Measurement, Reporting, and Verification
The use of satellite imagery and data from drones for mapping in the MRV process to track and assess carbon sequestration in forestry and agriculture. The MRV process (Measurement, Reporting, and Verification) is related to monitoring and evaluating carbon sequestration to register carbon credits.
Measurement, M
The collection and compilation of both qualitative and quantitative data are conducted according to specified formats or method that are widely accepted and standardized. This process is carried out using appropriate timeframes to support the preparation of greenhouse gas emissions accounting.
Reporting, R
Reporting data that has undergone a trustworthy verification process, approval, and authorization.
Verification, V
The verification and quality assurance of data to ensure that the reported information is accurate, complete, non-redundant, and maintains data consistency through reliable and globally accepted methods.
Verra
Verified Carbon Standard VCS
T-ver
Thailand Voluntary Emission Reduction Program
©ddm MRV
DDM Service
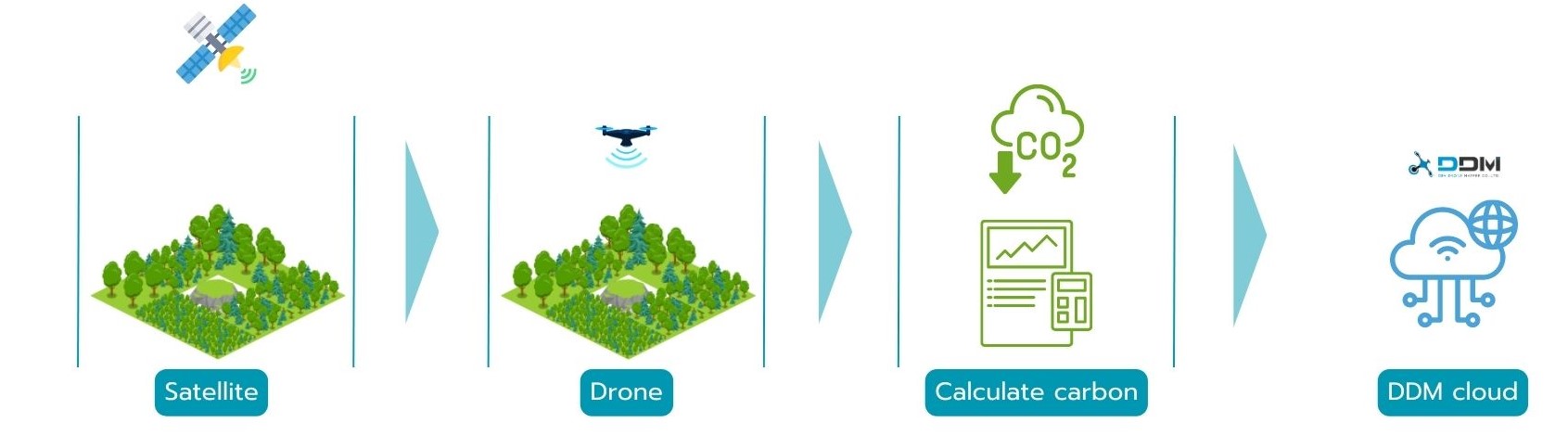
MRV (Measurement, Reporting, and Verification) is the process of measuring, reporting, and verifying carbon sequestration quantities. In this context, it will be carried out for forestry and agricultural activities. The measurement process begins with the use of remote sensing and geospatial technologies to generate data. It starts by utilizing satellite imagery capable of surveying large project areas to assess various aspects and identify the areas of interest. Subsequently, drone surveys are conducted to produce high-resolution aerial imagery maps, including orthomosaic and vegetation indices, which reveal the vegetation's health along with 3D models to measure tree height.
Once the initial data is obtained, the next step is field surveys for forest or agricultural plots to find representative sample areas. There are various methods available for laying out the sample plots, depending on suitability for each location. The final step involves calculating the carbon sequestration quantities, followed by preparing reports for the subsequent stages. DDM adheres to international standards and certified methodologies, including Verra (International) and T-ver (Thailand).
DDM (Data Delivery Mechanism) focuses on delivering cloud-based on a web portal format to prevent redundancy and ensure accessibility to all relevant project stakeholders. Throughout the data collection process,
Remote sensing Tool
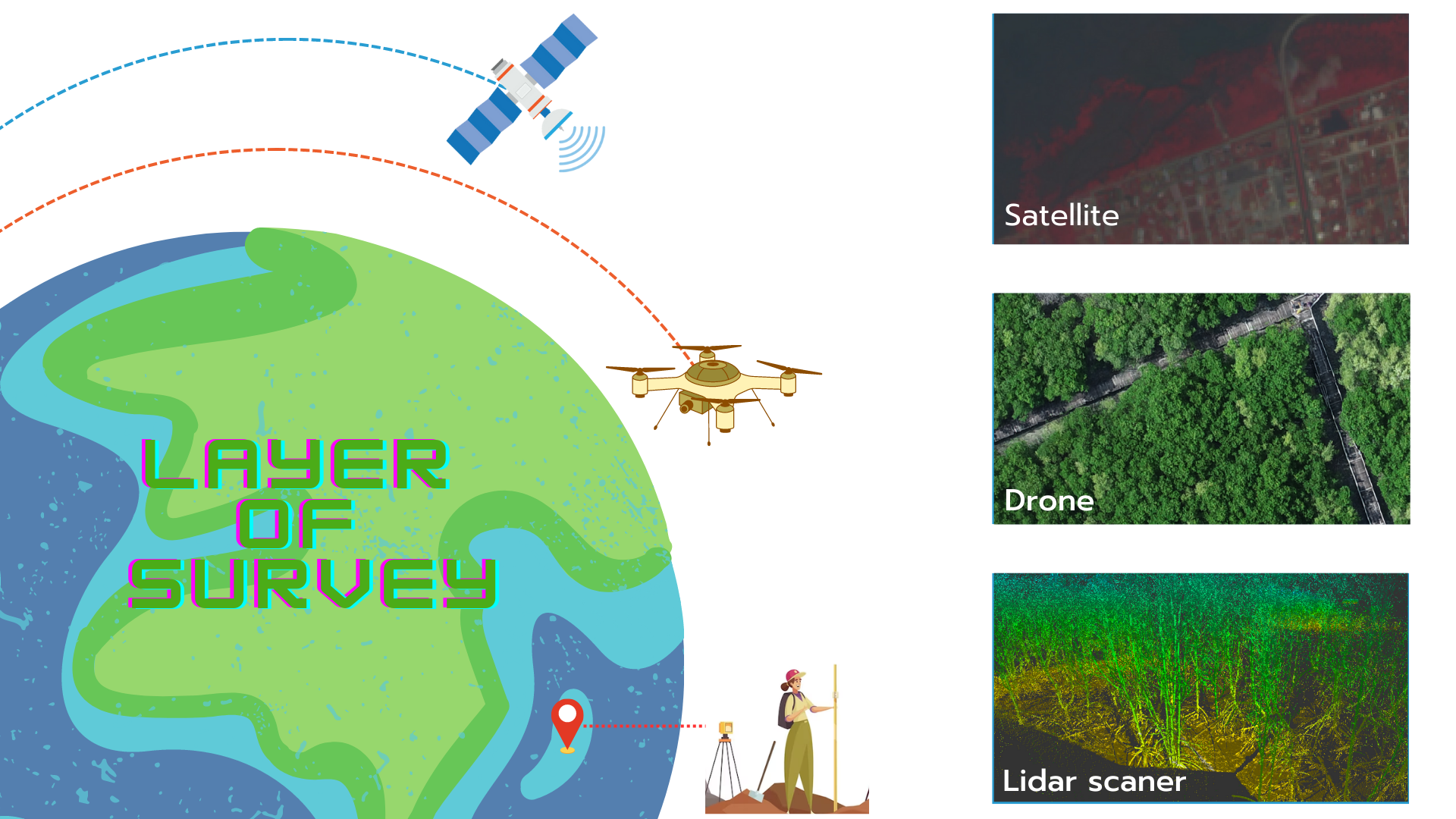
The use of remote sensing tools is essential in DDM (Data Delivery Mechanism) due to its specialized expertise in generating geo-spatial data. This expertise allows DDM to employ processes and knowledge for the measurement (M) and reporting (R) of carbon assessment in activities related to forestry and agriculture. The data preparation is in the form of maps, including aerial imagery maps, satellite images, and field survey data.
Satellite Data
Satellite imagery refers to photographs captured by satellites using sensors that record data through electromagnetic waves as data carriers. The data obtained from satellite imagery proves useful for various applications, such as terrain surveys, agriculture, and environmental monitoring.
The advantages of satellite imagery stem from its diverse data sources, which can be used without incurring additional costs. This makes it suitable for preliminary area surveys within the project overview. Satellite imagery also covers wide areas, enabling comprehensive surveys of multiple locations, thus saving time and project expenses. However, once the areas of interest are identified, drone surveys are conducted subsequently due to the limitations of satellite imagery, such as low resolution, which hinders the ability to observe finer details.
Drone Survey Data
Drone surveys involve capturing data using photogrammetry techniques, aiming to obtain photographs suitable for analysis and the creation of orthomosaic maps. These maps enable the analysis to generate Digital Surface Models (DSM) containing elevation data of the surveyed area. To ensure accurate data and appropriate analysis capability from drone imagery, the survey details are as follows
Aerial Photographic Maps
High-resolution aerial photographic maps that have undergone reconstruction processes (Model Photogrammetry) with processed data from Ground Control Points (GCP) to achieve spatial accuracy with a horizontal error of less than 5 centimeters and vertical error of less than 10 centimeters. The data is stored in .TIFF file format and can reference geographical coordinate systems and grid coordinate systems.
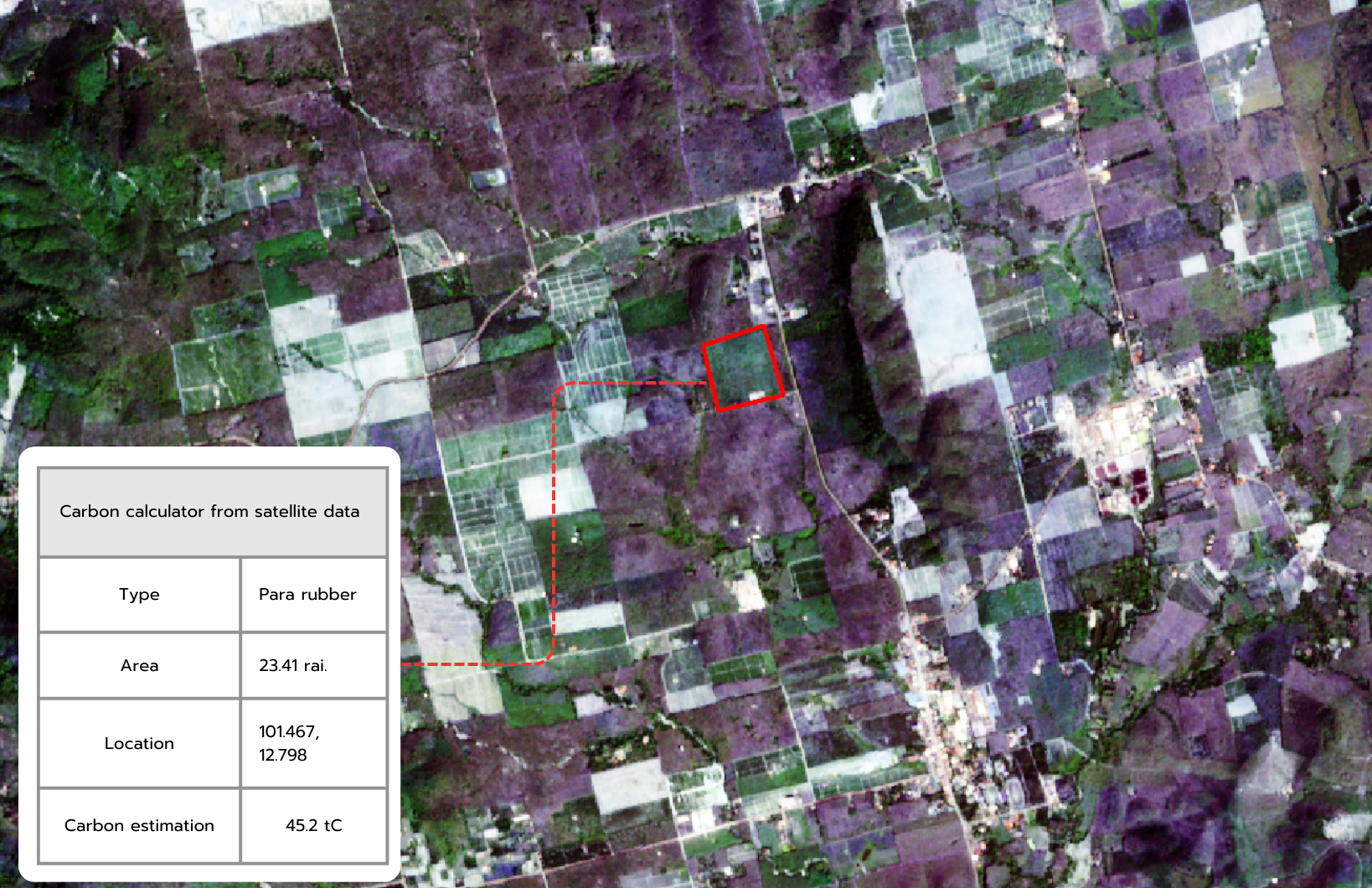
The high-resolution aerial photographic maps used for MRV (Measurement, Reporting, and Verification) in carbon assessment for forestry and agricultural project areas consist of two types: 1) High-resolution aerial photographic maps (Orthomosaic) and 2) Vegetation index (VI) data.
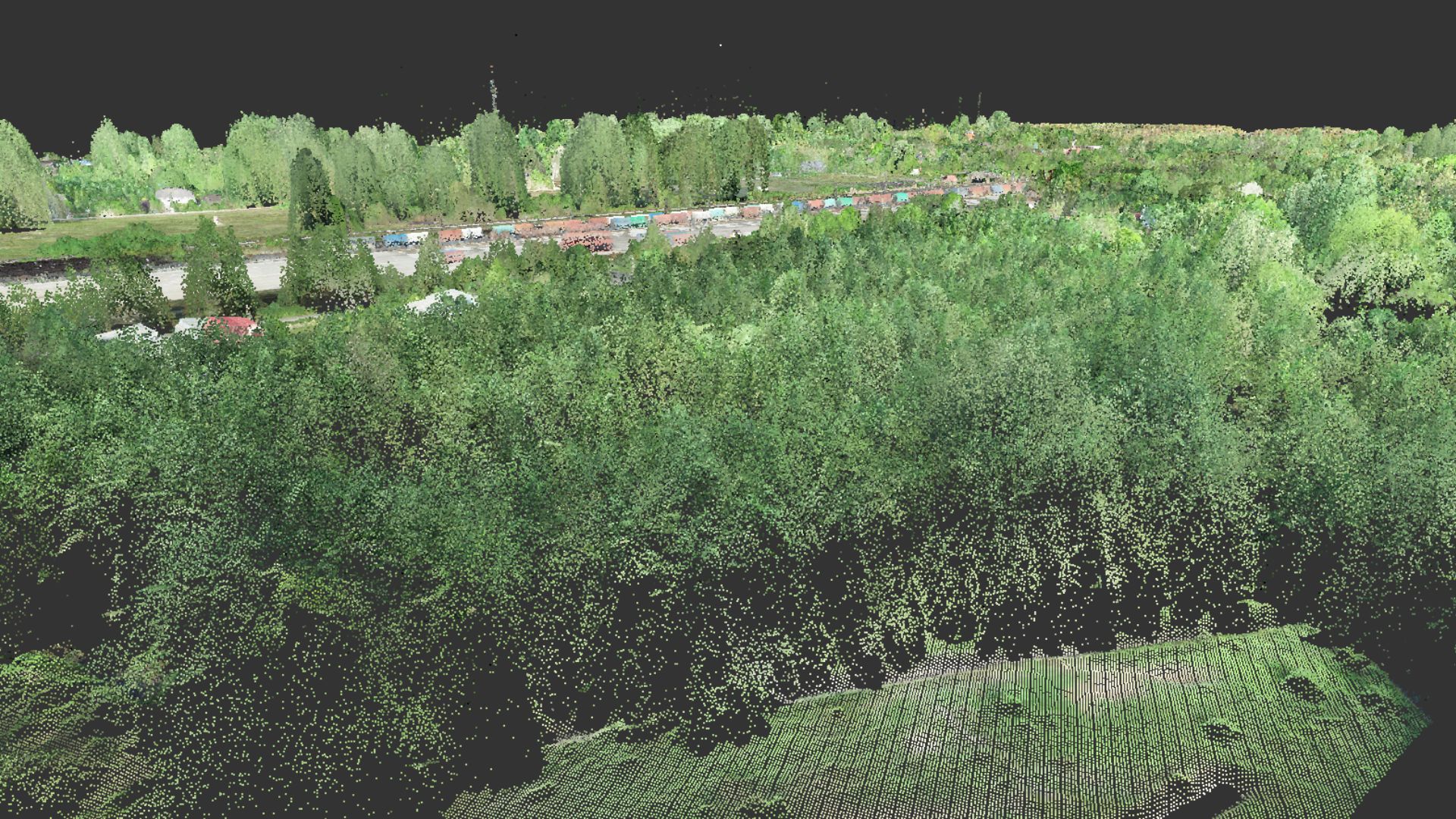
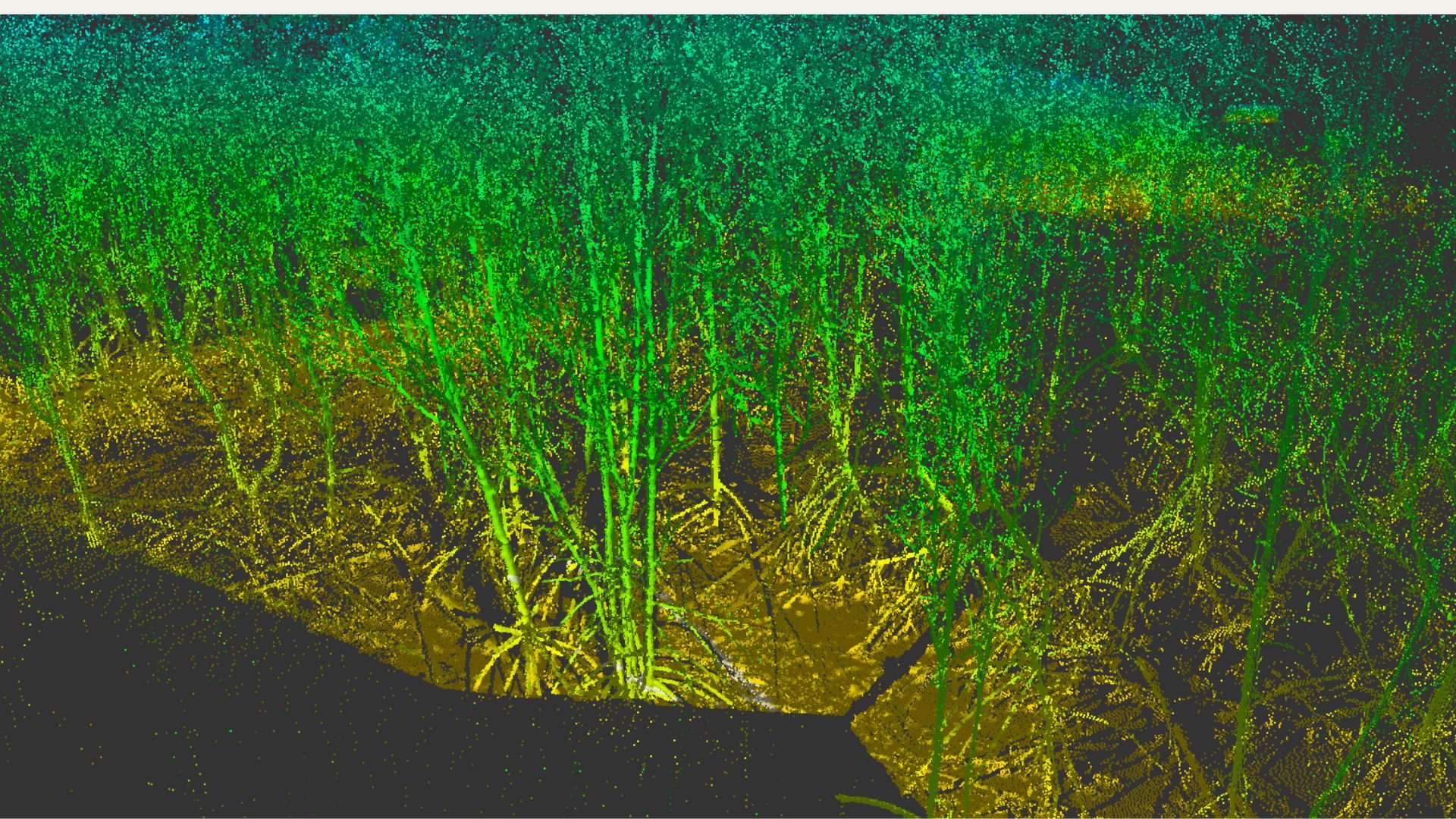
Point cloud
Point cloud is a representation of surveyed objects (e.g., trees in carbon assessment surveys) in a three-dimensional format. It is created by using a cluster of points that reflect the surface of the object and records the reflected point data in a coordinate system (x, y, z axes). Besides capturing point coordinate data, point cloud can also store spectral information or color data in RGB format, making it easier for human and computer systems to classify objects based on visual cues.
Point cloud data is utilized to classify the height of tree canopies by developing models that select the highest points of trees in proportion to the terrain's height. This allows for the estimation of tree height alone, reducing the field survey time for capturing tree height data and facilitating carbon sequestration assessment.
Data Delivery
Survey data and report data will be organized and stored in the FGDS format, accessible through a web map portal to facilitate access for relevant stakeholders in the project for further data utilization. The data presentation for carbon sequestration estimation includes aerial photographic maps, 3D terrain models, point cloud, and survey reports or carbon sequestration calculation reports. All data will be stored in a database system, allowing users to download the data via the internet. The data visualization for survey results and maps is developed using APIs and JavaScript libraries with reference coordinates, including latitude and longitude, displayed on the website, enabling users to interact with all data layers, such as panning, zooming in, and zooming out.
Application for carbon
DDM provides software development and application services for Carbon-related solutions. This includes applications that utilize Geo-spatial data, such as satellite imagery and location information, to create location-based software or applications. Additionally, DDM develops applications for measuring carbon emissions resulting from human activities, accessible through smartphones.
Team project
To achieve the objectives of the project, which involve data collection related to forestry and agriculture activities for carbon sequestration calculation, a smooth implementation, and the adoption of the DDM approach, a human resource management plan has been formulated for field survey activities. The plan includes one team comprising: [team composition details].
Survey Team Leader
The person responsible for conducting field data collection operations overall.
Drone operator
The person responsible for drone control in aerial photography mapping must possess a valid flight permit and must plan the flight to request authorization for the flight.
Drone Assistant Operator
Responsible for the aerial survey operation, including the drone's takeoff and landing, and assisting in the overall aerial surveillance of the area to prevent potential accidents.
Field Survey Officer
Responsible for field surveying to gather data used for aerial photography mapping and conducting tree sampling in sample plots.
Drone surveys pose significant risks and potential accidents. Therefore, DDM emphasizes strict compliance with regulations. The equipment used for surveys and the drone operators must have valid flight permits issued by the Department of Civil Aviation. Prior to each flight, authorization from the aviation radio company is also required to avoid any potential accidents.
DDM Certifiled
ISO 9001:2015
Quality Management Systems
Drone service and geo-spatial provider